Table of Contents
What is a character in python ?
A character in python is represented using a Unicode code point. A Unicode code point is written by using U+ followed by a number written in hexadecimal . This number written in hexadecimal represents a character , it has a min value of 0x0 and a max value of 0x10_ff_ff which is 1_114_111 in decimal . A Unicode code point hex_number can be represented by using 21 bits .
>>> max_unicode_hex_number = 0x10_ff_ff >>> max_unicode_hex_number.bit_length() 21
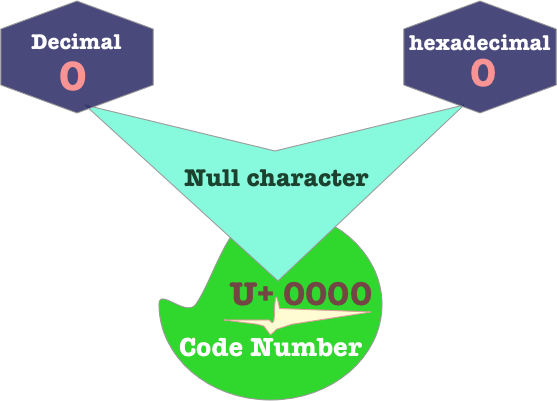
For example the Unicode point U+0000 represents the null character. 0000 is written in hexadecimal , it has a decimal and a hexadecimal value of 0 .
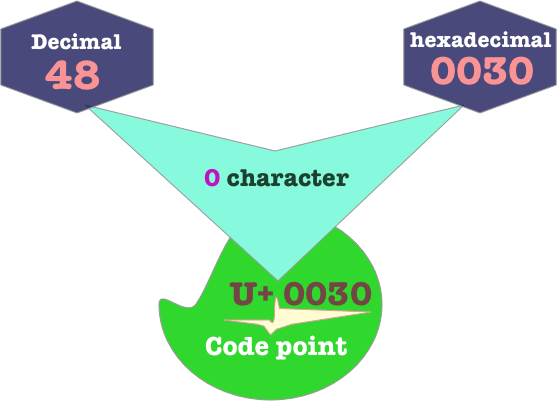
The Unicode point U+0030 represents the 0 character. 0030 is written in hexadecimal , it has a decimal value of 48 and a hexadecimal value of 30.
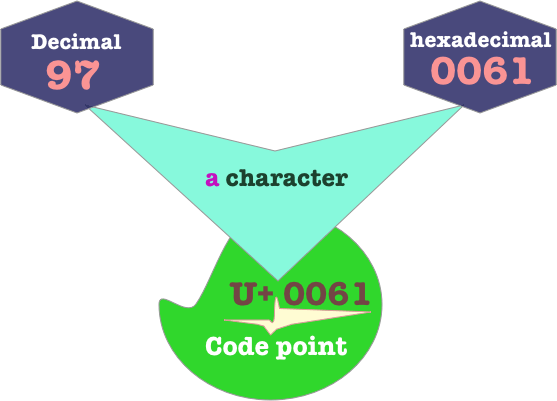
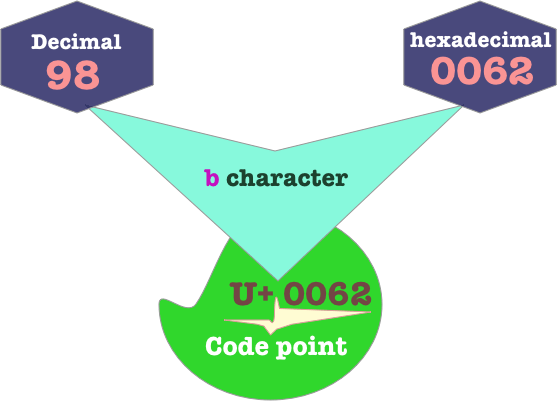
The Unicode point U+0061 represents the a character. 0061 is written in hexadecimal , it has a decimal value of 97 and a hexadecimal value of 61.
The Unicode point U+0062 represents the b character. 0062 is written in hexadecimal , it has a decimal value of 98 and a hexadecimal value of 62.
Get a character Unicode code point decimal value using ord
We can use the ord (character) function to get a character Unicode code point decimal value . So we will get the hexadecimal number in U+hex_number expressed in decimal .
>>> unicode_number_of_a = ord('a')
>>> unicode_number_of_a
97
>>> unicode_number_of_b = ord('b')
>>> unicode_number_of_b
98
Get a character Unicode code point hexadecimal number using hex
We can use the hex(ord (character)) function to get a character Unicode code point hexadecimal value . So to get the hex number in U+hex_number .
>>> hex_unicode_number_of_a = hex(ord('a'))
>>> hex_unicode_number_of_a
0x61
>>> hex_unicode_number_of_b = hex(ord('b'))
>>> hex_unicode_number_of_b
0x62
In this example the character a ( U+0061) Unicode code point hexadecimal number is 0x61 and the character b (U+0062) Unicode code point hexadecimal number is 0x62
Representing characters in python using a glyph
Characters that have a glyph or a symbol , can be represented in python by using a single , double or triple quote enclosing their glyph or symbol. The quotes must contain only one character . If they contain more than one character we will have a string .
>>> single_quote = 'a' >>> single_quote 'a' >>> double_quote = "b" >>> double_quote 'b' >>> triple_quote = '''c''' >>> triple_quote 'c'
In this example we have the characters a , b , and c which are represented using their glyph or symbols a b c .
Representing characters in python using an escape sequence
An escape sequence is enclosed in single , double or triple quotes , and it starts with the backslash character .
we may need an escape sequence either for :
- Representing characters that don’t have a glyph or symbol to represent them . For example a new line is represented in Unicode by the the Unicode code point
U+000A. A new line doesn’t have a glyph or a symbol to represent it , as such it is represented in python by using the escape sequence'\n'.>>> newLine_character = '\n' # A new line has no symbol to represent it. # We represent it using the escape sequence \n >>> ord(newLine_character) 10 # The new line character has a Unicode code point # of 10 in decimal
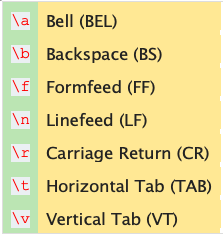
- Escaping characters that are used by python in a special way. For example :
- The single and double quote characters are used to represent a string , so to represent the single or double quote themselves , we must use an escape sequence
'\''"\"". - The backslash character is used to escape a sequence so to represent it itself , we must use an escape sequence
'\\'
- The single and double quote characters are used to represent a string , so to represent the single or double quote themselves , we must use an escape sequence
- Escaping something that can be interpreted by python in a special way . For example we can use the escape sequences
\u \U \x, to represent characters by their Unicode code point hex number . We can also represent characters by using an octal escape sequence , or by using their Unicode name .
Sometimes we don’t want an escape sequence to be interpreted in python . We can do this in two ways . We can either escape the backslash that starts an escape sequence with another backslash:
>>> escaping_an_escape_sequence = '\\a' # We can escape an escape sequence # by escaping the backslash that starts the # escape sequence by another one . # \\a , creates two characters # \\ is the backslash character which # has a Unicode code point of # U+005c . # a is the a character which has a # Unicode code point of of U+0061 >>> escaping_an_escape_sequence '\\a' >>> bell_character = '\a' # we didn't escape the escape sequence # \a by a preceding backslash . \a is # the bell character which has a Unicode # code point of U+0007
Or we can precede the string containing an escape sequence by an r –raw –. This has the same effect of preceding every backslash with another one , so we are escaping all the escape sequences .
>>> escaping_an_escape_sequence = r'\n\a' # escaping_an_escape_sequence is formed # of a backslash followed by the n # character followed by another backslash # followed by the a character >>> escaping_an_escape_sequence '\\n\\a' >>> print(escaping_an_escape_sequence) \n\a >>> escape_sequence = '\n\a' # escape_sequence is formed of # the new line character followed # by the bell character which has a # a Unicode code point of U+0007 >>> escape_sequence '\n\x07'
Representing characters in python by using \u \U \x
A character in python has a Unicode code point , which is formed of U+hex_number . Instead of representing character in python by using their glyph , we can represent them by using their Unicode code point hex_number .
A Unicode code point hex number has 21 bits . It has a min value of 0 and a max value of 0x10_ff_ff.
- When the Unicode code point hex number has a value between
0x0and0xff, we can represent it by using the\x,\uand\Uescape sequence . - When the Unicode code point hex number has a value between
0x0and0xff_ff, we can represent it by using the\u, and\Uescape sequence . - When the Unicode code point hex number has a value between
0x0and0x10_ff_ff, we can represent it by using the\Uescape sequence .
For example the z character has a unicode code point of U+007a . Its unicode code point hex number is less then or equal to 0xff as such we can represent it by using \x \u \U .
>>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number = '\x7a' >>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number 'z' >>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number = '\u007a' >>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number 'z' >>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number = '\U0000007a' >>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number 'z'
The ∂ character has a unicode code point of U+2202 , its hexadecimal number is 0x22_02 . It is larger than 0xff as such it cannot be represented by using \x , and it can only be represented by \u or \U .
>>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number = '\u2202' >>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number '∂' >>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number = '\U00002202' >>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number '∂'
The 𐅖 character has a unicode code point of U+10156 , its hexadecimal number is larger than 0xff_ff , hence it can only represented by using \U .
>>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number = '\U00010156' >>> character_represented_through_its_hex_number '𐅖'
Representing characters By using octal
We can represent characters which have unicode code point between U+0000 and U+00FF by using an octal escape sequence . The octal escape sequence is a backslash followed by three octal numbers .
For example the letter ÿ , has a code point of U+00FF , its hexadecimal number is FF which is 377 in octal as such we can represent it by using the octal escape sequence \377 .
>>> character_represented_through_an_octal_escape_sequence = '\377' >>> character_represented_through_an_octal_escape_sequence 'ÿ'
Representing characters using their unicode name \N{name}
We can represent characters in python by using their unicode name . We can use the unicodeData file to get the unicode name of a character or we can use the unicodedata module .
The unicodeData file contain the properties of the unicode characters .
03C4;GREEK SMALL LETTER TAU;Ll;0;L;;;;;N;;;03A4;;03A4 # The unicode code point 03C4 has a name of # GREEK SMALL LETTER TAU . its category is Ll # which is letter lowercase . It has a # bidirectional class of L , which is left to # right . N means that this character cannot # be mirrored as in using a mirror . For example # ( is mirrored to ) . # its uppercase is T and it has a unicode code point # of 03A4 , and its title case is T and it has a # hexadecimal number of 04A4
We can also use the unicodedata module to get the unicode properties of a character .
>>> import unicodedata
>>> unicodedata.name('τ')
# get the unicode character name of τ
'GREEK SMALL LETTER TAU'
>>> unicodedata.bidirectional('τ')
# get the bidirectional class of τ ,
# it is L which means Left to Right
'L'
>>> unicodedata.category('τ')
# get the unicode category of τ
# it is 'Ll' , which means
# letter lower case
'Ll'
So if we want to write a character using its unicode character name , we can do it like this .
>>> import unicodedata
>>> unicodedata.name('a')
'LATIN SMALL LETTER A'
>>> charachter_a = '\N{LATIN SMALL LETTER A}'
# use the escape sequence \n{name} to represent
# the character a
>>> charachter_a
'a'
>>> unicodedata.name('p')
'LATIN SMALL LETTER P'
>>> charachter_p = '\N{LATIN SMALL LETTER P}'
# use the escape sequence \n{name} to represent
# the character p
>>> charachter_p
'p'
What is encoding ?
A character has a Unicode code point. Its code point is formed of U+hex_number. The hexadecimal number has a min value of 0 , and a max value of 0x10_ff_ff and it has a max length of 21 bits .
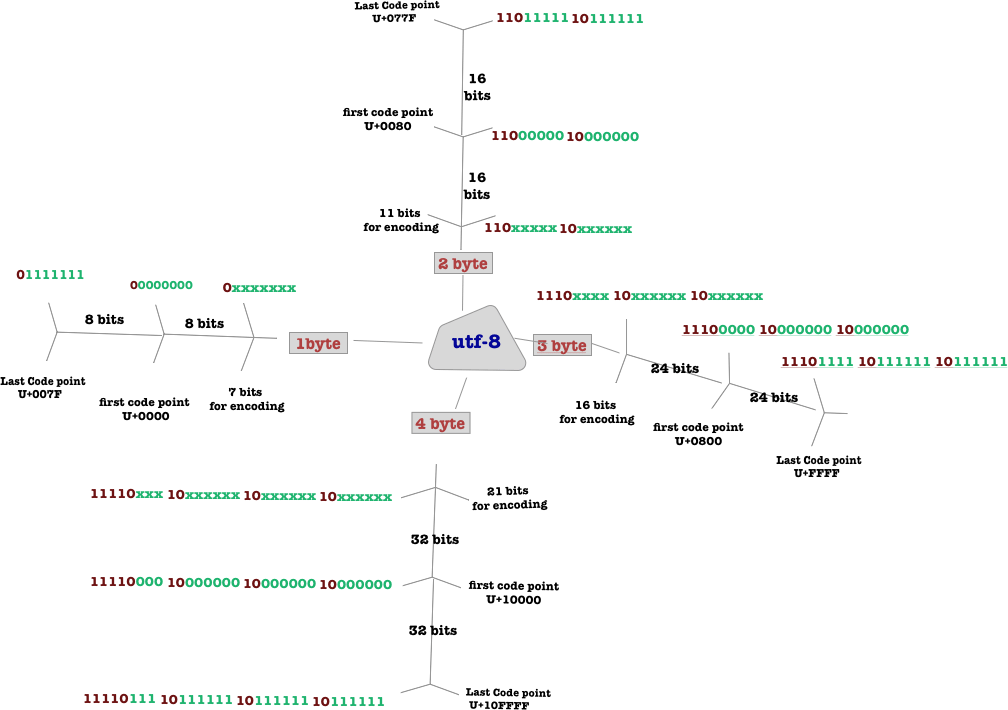
Encoding is how we are going to represent these 21 bits in computer. There are three encoding schemes , and they are
Utf-32which is about encoding the unicode code point hex number by using 32 bit . As such we only need one utf-32 unit to encode it.Utf-16, which is about encoding the unicode code point hex number by using 16 bits .As such we need 1 or two utf-16 units to encode it .Utf-8which is about encoding the unicode code point number by using 8 bits . As such we need one , two , three or four utf-8 units to to encode it . The next picture summarizes how to encode unicode code points by using utf-8 .
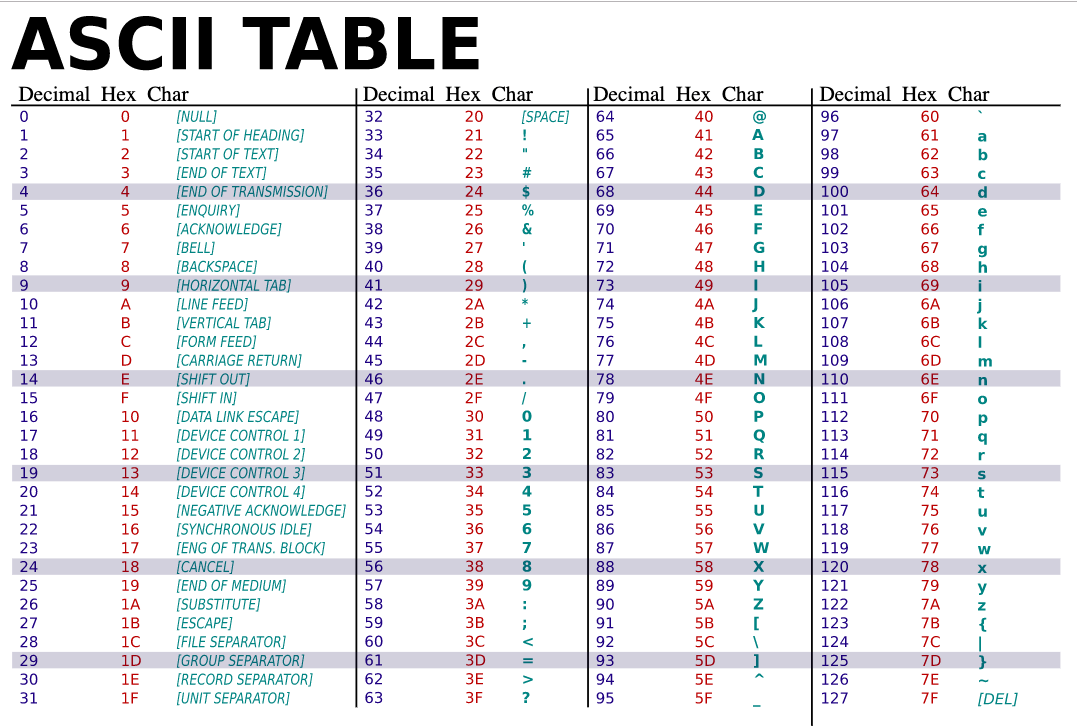
what is ascii ?
ASCII stands for American standard code for information interchange . It is an encoding of characters by using only 7 bits . It has a min value of 0 and a max value of 127 . The encoding is done on a byte , as such the first bit is always 0. ASCII encoding and Unicode code points between 0 and 127 are the same .