Table of Contents
What is a service
A service is simply code which is running , and this code , does not have a GUI . The code runs , on the main thread of its application (hosted process) , unless the code creates , a runnable thread , or is run in a separate process .
The code can either show a notification indicating that it is running , in such a case , it is foreground code . A notification , must be shown when accessing , for example the microphone , or the camera .
The code can show no indication , that it is running , in such a case , it is background code , like for example , emptying the cache folder of an application .
The code can be interacted with , like for example to send a specific request , or to receive a given result . In such a case , the code is available , as long , as the code that it is interacting with , is available . This is bound code .
A code can be bound , and show a notification , or show no notification , or a code can be unbound , and show a notification , or show no notification .
A service , so the code that can be bound , or unbound , or showing , or not showing a notification , is created using the Service class , and is started using an Intent .
Service lifetime and lifecycle
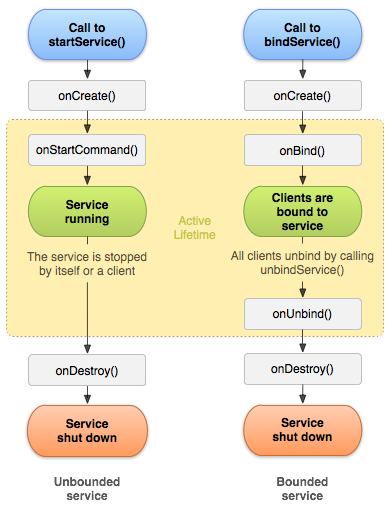
The code of an instance of a class , has a life time , which is the period during which the instance exists . So a service also , has a lifetime .
A lifetime has a cycle , which is when the instance is first created , lastly destroyed , and what happens in between.
From android developers , the service lifecycle is as follows :
public class ServiceLifeCycle extends Service {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
/* This method is only called once ,
when the service is being created ,
before onStartCommand or onBind
are called .*/ }
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
/* When a call to the startService
method is made ,
this method is called .
It must return a lifetime flag ,
which control the lifetime of
a service , started using startService .*/
return startMode; }
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
/* When a call to the bindService
method is made , this method
is called .*/
return binder; }
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
/* All clients have unbound
by calling the unbindService
method .*/
return allowRebind; }
@Override
public void onRebind(Intent intent) {
/* A client is binding to the service
by calling the bindService method ,
after the onUnbind method
has been called .*/ }
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
/* This method is called , when the
service is being destroyed . It
should be used to clean any
resources , for example
threads .*/ }
int startMode;
/* A lifetime flag , which indicates
how to behave if the service is
killed .*/
IBinder binder;
/* interface for clients that bind .*/
boolean allowRebind;
/* indicates whether onRebind should
be used .*/ }
So for example , when startService is called , the code specified in onStartCommand will get executed , and it can be used to show a notification , so the service will be a foreground service , or no notification , so the service will be a background service .
After that , a call to bindService , can be made . The code specified in onBindService , will get executed . It must return an interface , which allows communication with a code . The code is bound to the lifetime of the clients , hence this is known as a bound service .
Lifetime flags
An instance of a Service , can have some flags set to it . These flags control the lifetime of the instance , of the Service .
These flags are only applicable , to a service which is started by calling startService . A service which has only the bindService() method called , is destroyed , when all the bound clients , have unbound .
The START_STICKY flag states , that when an instance of a Service is destroyed , for example on low memory , another instance of this service , will be created , as such the onCreate , and on onStartCommand will be called . The executing code is restarted from scratch , and no state is preserved . The original Intent , which started the first instance of the Service , is not re-passed to the onStartCommand , hence it is null .
The START_REDELIVER_INTENT flag dictates , that when an instance of a Service is destroyed , what happens , is that another instance of the Service is created . The executing code , is restarted from scratch , the onCreate , and onStartCommand functions are executed , in this case , the onStartCommand will receive the original Intent , that started the earlier instance , of the service .
The START_NOT_STICKY flag states , that when an instance of a Service is destroyed , it is not recreated , so it must be manually recreated .
A service which is showing a notification , has the same priority as an application which is running in the foreground , so it is less likely that it will be killed on low memory , but the important thing to remember , is that this is not important .
Registering a service
A Service must be declared in the manifest of an application , by adding a service element , as a child , to the application element .
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8" ?>
<manifest
xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package = "com.twiserandom.mobileapps.demo.coding_demo" >
...
<uses-permission
android:name = "android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE" />
<application ... >
<service
android:name = "string"
android:foregroundServiceType = "camera | connectedDevice |
dataSync | location | mediaPlayback |
mediaProjection | microphone | phoneCall"
android:process="string" >
. . .
</service>
...
</application>
</manifest>
If the service is a foreground service , then uses-permission foreground service , must be specified in the manifest .
Also if the service is a foreground service , then using foregroundServiceType , it must state its type , which can be one or more , for example camera , or camera | microphone
The only required attribute , is the name attribute , which specifies the name of the class , that implements the service . The name of the class can either be fully qualified , by specifying the package to which this class belongs , or it can start with a dot . , in this case , it belongs to the package specified in the manifest .
A service can run on a different process , then the default process , created for the application , by using the process attribute . If the string name , in the process attribute , starts with a colon : , then the service will run in a newly created process , private to its application . If the string name , starts with a lower case letter , than the service will run in a global process , having the indicated name .
Starting , and stopping a service
A service can be started by calling startService , a service started by calling startService , is called a started service .
Intent intent = new Intent (this , Service_ClassName.class ); startService (intent );
Data can be added to an intent , like to specify some options , to the Service .
Intent intent = new Intent (this , Service_ClassName.class );
intent .putExtra ("do" , "what" );
intent .putExtra ("what-arg" , 0.5 );
startService (intent );
The startService method , can be called multiple times , as such the onStartCommand , can also be called multiple times .
A service started using the startService method , can be stopped using the stopService method .
Intent intent = new Intent (this , Service_ClassName.class ); stopService (intent );
It can also stop itself , using : stopSelf (int startId ) . The startId in stopSelf , is the one received from the onStartCommand . It is used to prevent the service from stopping itself , if new startService calls , have been issued , but if the most recent startId is used , then the service will stop itself , disregarding any previous startService calls .
A started service can display a notification that it is running , and promote itself to a foreground service , by using the startForeground method , which takes as parameters , a user defined notification id , and the actual notification , to display to the user .
startForeground (int id, Notification notification)
To demote a foreground service , back to being a background service , the stopForeground method can be called . This does not stop the service from running . The stopForeground method , can also be passed a boolean true , to remove any displayed notifications . Now that the service is demoted , to being back a background service , it can be stopped as explained earlier , using stopSelf , or stopService .
A service can be started by calling the bindService method , which has the following signature :
public abstract boolean bindService (Intent intent,
ServiceConnection events,
int options)
The intent is just a regular intent to start a service , as shown earlier .
events , is just an instance of an interface , which must respond to the different binding events , that occurs , for example , onBindingDied , or onServiceConnected , or onServiceDisconnected .
options is just the options to control the binding process , for example the flag BIND_AUTO_CREATE , will automatically create the service .
If the service class exists , and the client is allowed to bind to it , the bindService method , returns true , otherwise it returns false .
When the binding is being performed , the onBind method is called , and it must return an instance of the IBinder interface . Binding is more related to interprocess communication , so to communicate between different process , but can be used in all cases . The binder class , implements the methods , that allow performing the interprocess communication , and we can extend it , to provide our own methods , as a service to a client .
A bound service , can be unbound , and stopped by using the unbindService method .
A service which has only its bindService method called , is automatically destroyed , when all the bound clients unbind , so after the onUnbind method is called .
If a service has been started using the startService method , and also started using the bindService method , then calling the stopService or stopSelf methods , will not destroy this service , until all bound clients have unbound , and vice versa , when all clients have unbound , but the stopSelf or stopService methods , have not been called , the service will not be destroyed .
Getting results from a service
A service started using the startService method , can use for example a toast , or a notification , or a broadcast … to provide or show some results . It can also be made bound , in order to retrieve results when necessary .
Demo application
This application illustrates all the points , talked about earlier . It has three services , one is used to purge the content of the cache directory , the second is used to record audio , and the third is used to interact with some code , so just to calculate the addition of n numbers , and to stop a started recording session .
The Service source code is as follows :
package com .twiserandom .mobileapps .demo .coding_demo;
import android .app .Notification;
import android .app .NotificationChannel;
import android .app .NotificationManager;
import android .app .Service;
import android .content .Intent;
import android .media .MediaRecorder;
import android .os .Binder;
import android .os .CountDownTimer;
import android .os .IBinder;
import android .util .Log;
import android .widget .Toast;
import androidx .localbroadcastmanager .content .LocalBroadcastManager;
import java .io .IOException;
import java .nio .file .DirectoryStream;
import java .nio .file .Files;
import java .nio .file .LinkOption;
import java .nio .file .Path;
import java .util .UUID;
public class Service_Demo extends Service {
final String fnlStr_debug_tag = "Service Demo Debug";
IBinder binder ;
boolean allowRebind = false;
boolean stop_recording = false;
Thread thr_rmCache , thr_recordSound;
@Override
public void
onCreate() {
binder = new LocalBinder ( ); }
@Override
public int
onStartCommand (Intent intent , int flags , int startId ){
if(intent == null ){
/* The service has been killed , and the startMode
has been set set to START_STICKY . As such
the service is now being restarted , with a
null Intent , so the original intent
is not delivered again .
When START_STICKY is set , the intent
itself is not primordial , for the
service to run .*/
thr_rmCache = new Thread (new Purge_Cache (startId ) ) ;
thr_rmCache .run();
return START_STICKY; }
else {
/*An intent has been delivered . Either , the service
is starting fresh , or it has been killed , and
its start mode has been set to START_REDELIVER_INTENT .
So the original intent is being redelivered .*/
switch (intent .getStringExtra ("do" ) ){
case "Clear Cache":
if (thr_rmCache == null ){
thr_rmCache = new Thread (new Purge_Cache (startId ) ) ;
thr_rmCache .run();
return START_STICKY; }
break;
case "Record Sound" :
if (thr_recordSound == null ){
thr_recordSound = new Thread (new Record_Sound ( ) );
thr_recordSound .run ( );
return START_REDELIVER_INTENT; }
break; } }
return START_NOT_STICKY; }
@Override
public IBinder
onBind(Intent intent ){
/* extras are not delivered
on binding , unbinding , or
rebinding .
The intent delivered ,
on binding , unbinding ,
rebiding , is the original
intent delivered when
binding .*/
return binder; }
@Override
public boolean
onUnbind(Intent intent) {
return allowRebind; }
@Override
public void
onRebind(Intent intent) { }
@Override
public void
onDestroy( ) {
if (thr_rmCache != null && thr_rmCache .isAlive ( ) )
thr_rmCache .interrupt ( );
if (thr_recordSound != null )
stop_recording = true ; }
/* A class to Purge the cache directory ,
* it will show a toast when starting ,
* the process , and when it is done
* doing its job , it will show a
* notification , and send a local
* broadcast .*/
class Purge_Cache implements Runnable {
int startId;
public
Purge_Cache (int starId ){
this .startId = starId; }
@Override
public void
run ( ){
//show a toast on start
Toast .makeText(Service_Demo .this ,
"Clearing the cache directory" , Toast .LENGTH_LONG ) .show ( );
//purge the cache
purge_Cache (getCacheDir ( ) .toPath ( ) );
//show a notification after cash is purged
cleared_Cache_Notification ( );
//Create a local broadcast
Intent intent = new Intent ("Cache Purged" );
intent .putExtra ("msg" , "The cache is purged" );
LocalBroadcastManager .getInstance (Service_Demo .this .getApplicationContext ( ) )
.sendBroadcast (intent );
//done
thr_rmCache = null;
if (thr_recordSound == null )
stopSelf (startId ); }
public void
purge_Cache (Path pathD ){
//Do not remove the directory , only its content recursively
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , pathD .toString ( ) );
if (Thread .interrupted ( ) ){
return ;}
try (DirectoryStream<Path > paths =
Files .newDirectoryStream
(pathD ) ){
for (Path td_path : paths ){
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , td_path . toString ( ) );
if (Files .isDirectory
(td_path , LinkOption .NOFOLLOW_LINKS ) ){
purge_Cache (td_path ); }
Files .delete (td_path ); }}
catch (IOException | SecurityException exception ){
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , exception .toString ( ) );}}
public void
cleared_Cache_Notification ( ){
//Create notification channel
String notification_channel_id = "coding_demo_cache_purged";
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel (notification_channel_id ,
"coding demo cache purged" , NotificationManager .IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT );
channel .setDescription ("Coding demo cache purged channel" );
NotificationManager notificationManager = getSystemService (NotificationManager .class );
notificationManager .createNotificationChannel (channel );
//create notification
int notification_id = 1;
Notification .Builder notification_builder = new Notification
.Builder (Service_Demo .this , notification_channel_id )
.setSmallIcon (R .mipmap .ic_launcher )
.setContentTitle ("Code demo" )
.setContentText("The application cache is cleared" );
notificationManager .notify (notification_id , notification_builder .build ( ) ); } }
/* Record sound class
*/
class Record_Sound implements Runnable{
CountDownTimer audioCapture_countDownTimer;
MediaRecorder audioCapture_recorder;
int audioCapture_duration = 25;
@Override
public void
run ( ) {
Toast .makeText(Service_Demo .this , "Starting to record Sound !" ,
Toast .LENGTH_SHORT ) .show ( );
start_Recording ( );
startForeground (2 , sound_Recording_Notification ( ) );
}
public void
start_Recording ( ) {
try {
//Start recording
String audioCapture_fileName = getCacheDir( ) .getAbsoluteFile( )
+ "/" + UUID .randomUUID( ) .toString( ) + ".m4a";
audioCapture_recorder = new MediaRecorder ( );
audioCapture_recorder .setAudioSource (MediaRecorder .AudioSource .MIC ) ;
audioCapture_recorder .setOutputFormat (MediaRecorder .OutputFormat .MPEG_4 );
audioCapture_recorder .setAudioEncoder (MediaRecorder .AudioEncoder .AAC );
audioCapture_recorder .setAudioSamplingRate (44100 );
audioCapture_recorder .setAudioChannels (2 );
audioCapture_recorder .setAudioEncodingBitRate (32000 );
audioCapture_recorder .setOutputFile (audioCapture_fileName );
audioCapture_recorder .prepare ( );
audioCapture_recorder .start ( );
//Cancel recording after audioCapture_duration , or on interrupt
audioCapture_countDownTimer = new CountDownTimer (audioCapture_duration * 1000 , 1000 ){
public void
onTick(long millisUntilFinished ){
if(stop_recording ){
audioCapture_countDownTimer .cancel ( ) ;
stop_Recording ( ); }}
public void
onFinish ( ){
Toast .makeText(Service_Demo .this ,
"Finished recording audio" , Toast .LENGTH_SHORT ) .show();
stop_Recording ( ); }};
audioCapture_countDownTimer .start( ); }
catch (Exception exception ){
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , exception .toString ( ) );
Toast .makeText(Service_Demo .this , "Failed to record sound "
, Toast .LENGTH_SHORT ); }}
public void
stop_Recording ( ){
audioCapture_recorder .stop( );
audioCapture_recorder .release( );
thr_recordSound = null ;
stop_recording = false ;
stopForeground (true ); }
public Notification
sound_Recording_Notification ( ){
// Create notification channel
String notification_channel_id = "coding_demo_audio_capture";
NotificationChannel channel = new NotificationChannel (
notification_channel_id , "coding demo audio capture" ,
NotificationManager .IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT );
channel .setDescription("Coding demo audio capture channel" );
NotificationManager notificationManager = getSystemService (NotificationManager .class );
notificationManager .createNotificationChannel (channel );
// Create the notification
Notification .Builder notification_builder = new Notification
.Builder (Service_Demo .this , notification_channel_id )
.setSmallIcon (R .mipmap .ic_launcher_round )
.setContentTitle ("Code demo" )
.setContentText ("Sound is being recorded" );
return notification_builder .build ( ); }}
class LocalBinder extends Binder{
public int
add (int ... vars_i ){
int sum = 0;
for (int var_i : vars_i ){
sum += var_i ; }
return sum ; }
public void
stopRecordSound (){
if(thr_recordSound != null ){
stop_recording = true ;
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , "Audio recording is stopped " ); }}}}
The main activity source code is as follows :
package com .twiserandom .mobileapps .demo .coding_demo;
import androidx .annotation .NonNull;
import androidx .appcompat .app .AppCompatActivity;
import androidx .localbroadcastmanager .content .LocalBroadcastManager;
import android .Manifest;
import android .content .BroadcastReceiver;
import android .content .ComponentName;
import android .content .Context;
import android .content .Intent;
import android .content .IntentFilter;
import android .content .ServiceConnection;
import android .content .pm .PackageManager;
import android .os .Bundle;
import android .os .IBinder;
import android .util .Log;
import android .view .View;
import android .view .ViewGroup;
import android .widget .Button;
import android .widget .LinearLayout;
import android .widget .Toast;
public class Activity_Main extends AppCompatActivity {
final String fnlStr_debug_tag = "Activity Main Debug";
final int fnlInt_request_audio_permissions = 1013;
final Button_Model arr_btnModels [ ] = {
new Button_Model (Button_Model .fnlStr_code_notification ) ,
new Button_Model (Button_Model .fnlStr_code_noNotification ) ,
new Button_Model (Button_Model .fnlStr_codeBound_notification_noNotification ) } ;
@Override
protected void
onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState ){
super .onCreate (savedInstanceState );
create_Interface ( );
register_Broadcast_Receiver ( ); }
public void
create_Interface( ){
LinearLayout ll = new LinearLayout (this );
ll .setOrientation (LinearLayout .VERTICAL);
Click_Listener_Buttons click_listener_buttons = new Click_Listener_Buttons ( );
Button btn ;
for (Button_Model btnModel : arr_btnModels ){
btn = new Button (this ) ;
btn .setText (btnModel .btn_text );
btn .setTag (btnModel .btn_text );
btn .setOnClickListener (click_listener_buttons );
ll .addView (btn ,
ViewGroup .LayoutParams .MATCH_PARENT ,
ViewGroup .LayoutParams .WRAP_CONTENT ); }
setContentView(ll ); }
public void
register_Broadcast_Receiver ( ){
CachePurged_Receiver cachePurged_receiver = new CachePurged_Receiver ( );
IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter ("Cache Purged" );
LocalBroadcastManager .getInstance (getApplicationContext ( ) )
.registerReceiver (cachePurged_receiver , intentFilter );
}
/*Cache Purged Receiver Class */
class CachePurged_Receiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void
onReceive(Context context, Intent intent ){
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , "Cache Purged Broadcast Received" );
Toast .makeText (context , intent .getStringExtra ("msg" ) ,
Toast .LENGTH_LONG ) .show ( ); }}
/* Buttons Click Listeners class */
class Click_Listener_Buttons implements View .OnClickListener{
Service_Demo .LocalBinder localBinder;
Service_Connection service_connection;
@Override
public void
onClick(View view ){
Intent intent = new Intent (Activity_Main .this , Service_Demo .class ); ;
switch ((String ) view .getTag( ) ){
case Button_Model .fnlStr_code_noNotification:
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , "running some code without a notification" );
//start service purge cache
intent .putExtra ("do" , "Clear Cache" );
startService (intent );
break;
case Button_Model .fnlStr_code_notification:
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , "running some code showing a notification" );
//check for permissions
if (checkSelfPermission (Manifest .permission .RECORD_AUDIO ) == PackageManager .PERMISSION_GRANTED ){
// granted start audio recording service
intent .putExtra ("do" , "Record Sound" );
startService (intent ); }
else{
// not granted , request the permissions
requestPermissions (new String [ ]{Manifest .permission .RECORD_AUDIO } ,
fnlInt_request_audio_permissions );}
break;
case Button_Model .fnlStr_codeBound_notification_noNotification:
/* Click the third button , which is this switch case ,
only after starting an audio recording service ,
since it will automatically stop it ,
If you click it a second time , it is not necessary ,
to start recording , it will just unding the service . */
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , "Bound code interacting with code showing and not showing a notification" );
if (service_connection != null ){
unbindService (service_connection );
service_connection = null; }
else{
service_connection = new Service_Connection ( );
bindService(intent , service_connection , Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); }
break; } }
class Service_Connection implements ServiceConnection{
@Override
public void
onServiceConnected (ComponentName name , IBinder service){
// Called when binding has been established .
localBinder = (Service_Demo .LocalBinder ) service;
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , "" + localBinder .add (1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ) );
// call the add method in the bound service .
localBinder .stopRecordSound();
/* Stop sound recording in the bound service */ }
@Override
public void
onServiceDisconnected (ComponentName name ){
//Called when binding is lost .
localBinder = null; }
@Override
public void
onBindingDied (ComponentName name ){
// Called when binding is dead.
localBinder = null; }
@Override
public void
onNullBinding (ComponentName name ){
// Called when onBind returns null
localBinder = null; } }}
@Override
public void
onRequestPermissionsResult (int requestCode , @NonNull String [ ] permissions , @NonNull int [ ] grantResults ){
super .onRequestPermissionsResult (requestCode , permissions , grantResults );
switch (requestCode ){
case fnlInt_request_audio_permissions :
if(grantResults .length > 0 && grantResults [0 ] == PackageManager .PERMISSION_GRANTED ){
//audio record permission has been granted
Intent intent = new Intent(Activity_Main .this , Service_Demo .class);
intent .putExtra ("do" , "Record Sound" );
startService (intent ); }
else{
Log .d (fnlStr_debug_tag , "Permission to record sound not granted" ); }}}
}
class Button_Model{
final static String fnlStr_code_noNotification = "Code no notification Service";
final static String fnlStr_code_notification = "Code notification Service";
final static String fnlStr_codeBound_notification_noNotification = "Code bound notification and no notification Service";
String btn_text;
public
Button_Model (String btn_text ){
this.btn_text = btn_text; } }
And the manifest source code is as follows :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.twiserandom.mobileapps.demo.coding_demo">
<uses-permission android:name = "android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".Activity_Main">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service
android:name = ".Service_Demo"
android:foregroundServiceType = "microphone">
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
IntentService
An IntentService , is a service which is an instance , of the IntentService class . The IntentService class is a subclass of the Service class .
The IntentService class , uses a single worker thread , when a call to startService is made , as not to implement one’s own thread . This thread is different from the application main thread .
Calls made to startService , are processed sequentially , on this newly created thread , one after another , and the IntentService automatically stops itself , when no more work is to be done .
IntentService is deprecated , and JobIntentService must be used instead .